Describe How to Acquire Radiographic Images Using Various Techniques
The chemical process done during processing is what brings out the image onto the film making it permanent so any mistake during this process can lead to faults in the Radiographic image. Describe patient preparation for radiographic exposures.

The Radiology Assistant Fracture Mechanism And Radiography Medical Radiography Ankle Fracture Radiography
RADIOGRAPHS Periapical Bitewing Occlusal.

. Demonstrate understanding of appropriate techniques for optimum radiographic image viewing. Film Radiography Real Time Radiography RTR Computed Tomography CT Digital Radiography DR and Computed Radiography CR. The differences in absorption are then recorded on films or through an electronic means.
When the film is parallel with the long axis of the tooth the image looks the same as the tooth itself. Identify anatomical structures dental materials and patient information observed on. NBDHE 20 Obtaining and Interpreting Radiographs NBDHE 21 Principles of radiophysics and radiobiology 15.
Describe use and purpose of various intraoral and extraoral radiographic images MSC. Video-based learning lessons classify radiographic equipment based on techniques such as digital and traditional radiography describe how to acquire radiographic images using various techniques identify current American Dental Association ADA guidelines for patient selection and limiting radiation exposure identify operator safety measures when acquiring x-rays. Apply the principles of radiation protection and hazards in the operation of radiographic equipment MSC.
Although originally developed to simulate X-Ray transmission radiography HADES has grown to simulate neutron radiography over a wide range of. And a thorough understanding of anatomy physiology pathology instrumentation artifact. The automatic weld defect detection in radio- graphy images has been studied by several researchers using various techniques and approaches 456789 10 11.
Traditionally the image was produced by the X-rays passing through an object the patient and interacting with the photographic emulsion on a film which resulted in blackening of the film. The processed image is a hard-copy film. Describe how to acquire radiographic images using various techniques CDA RHS IIIB.
Misinterpretations may occur due to image distortions and can be minimized by employing standardized techniques including specific film placement beam angulation and image processing to produce images that are good representations of the structures of interest. Select equipment for radiographic technique. Identify anatomical landmarks that aid in mounting.
Apply the principles of radiation protection and hazards in the operation of radiographic equipment. KVp controls radiographic contrast which is defined as the number of differences between shades of white black and gray in the image. NBDHE 25 General Your adolescent patient is scheduled for an orthodontic evaluation and needs a single radiograph of his side facial profile that includes his skeletal structure tissues jaws and teeth.
Select appropriate radiographic survey to examine or view conditions teeth or landmarks. Assessment of root formation n completion. Implant site assessment and.
3 different types film badge pocket dosemeter thermo luminescent device. A high degree of manual dexterity and hand-eye coordination. In a first stage image processing techniques including noise reduction contrast enhancement thresholding and labelling were implemented to help in the recognition of weld regions and the detection of weld defects.
NBDHE 20 Obtaining and Interpreting Radiographs NBDHE 21 Principles of radiophysics and radiobiology. Assessment of relationship of roots to various vital structures. Describe techniques for patient management while acquiring radiographic images including for patients with special needs.
A radiographic image is created using a number of steps. Assessment of root morphology. The latent image formed on the film is rendered visible through chemical processing.
There is no distortion. Include image distortion and excess radiation due to increased angulations exposing the eyesand thyroid. One method to obtain the tunnel view is to have the knee flexed 40-50 degrees with the patient prone and support placed under the tibia-fibula.
Describe how to mount radiographic images using facial buccal and labial view. Describe how to acquire radiographic images using various techniques CDA RHS IIIB. The ability to conceptualize two-dimensional 2D information into a three-dimensional 3D format.
The production of a high-quality sonographic image is an art that demands many talents of the sonographer. Processing of a Radiograph is the term used to describe the steps which are done using chemicals to process or develop a film which has been exposed to X-rays. Match tooth views to tooth mount windows.
Describe patient preparation for radiographic exposures Describe use and purpose of intraoral and extraoral radiographic images Select appropriate radiographic survey to examine or view conditions teeth or landmarks Describe technique modifications based on anatomical variations and clinical conditions Select equipment for radiographic technique Describe how to acquire. HADES is a code that simulates radiography using ray tracing techniques. Describe use and purpose of intraoral and extraoral radiographic images.
There are two different radioactive. This module provides a thorough introduction to basic radiographic techniques and demonstrates how to set up and perform an X-ray procedure. Describe how to mount radiographic images using facial buccal and labial view.
The image receptor is centered on the central ray. Nature of the radiographic image. Radiographic assessment may employ either film or digital receptors.
First the patient is exposed to a predetermined amount of radiation to provide the required diagnostic image quality. Paralleling technique provides less image distortion and reduces excess radiation to the patient. Describe technique modifications based on anatomical variations and clinical conditions.
133134 To the eye contrast is the number of different shades seen between the darkest black and the lightest white in the image. To produce an optimal image a certain amount of contrast is necessary so that. In this paper we describe an automatic classification system of welding defects in radiographic images.
Radiographic technologists assist in the diagnosis and management of human illness by producing diagnostic images also called radiographs or X-rays of relevant patient anatomy. Film is gradually being replaced by a variety of digital sensors with the image being created in a computer. Periapical views are used to record the crowns roots and surrounding bone.
It is often useful to simulate radiographic images in order to optimize imaging trade-offs and to test tomographic techniques. For a lateral view the patient is positioned on the affected side with the knee flexed 20-30 degrees. In industrial radiography there are several imaging methods available techniques to display the final image ie.

Endodontic Radiology Pocket Dentistry
Radiographic Techniques Radiology Key
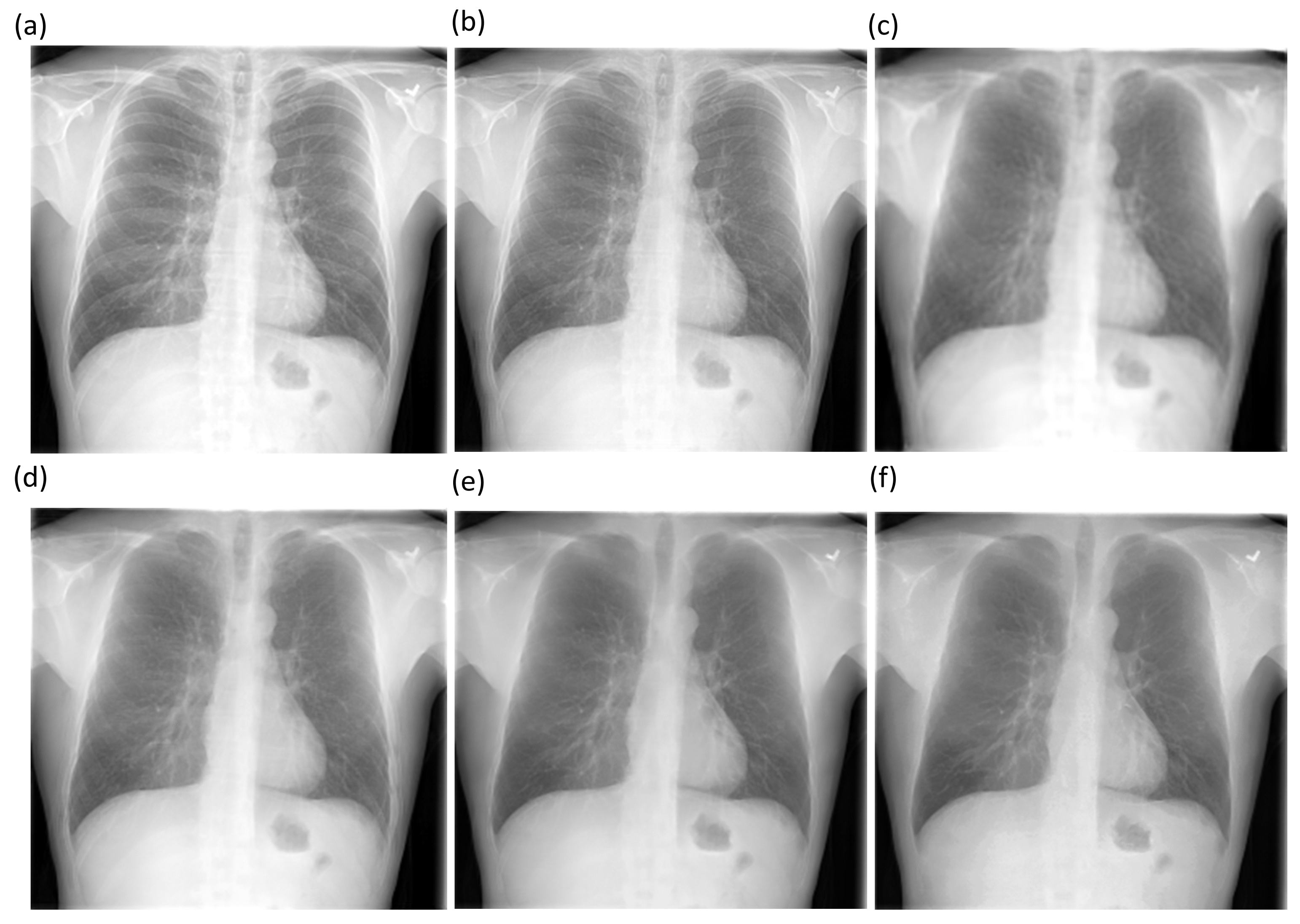
Diagnostics Free Full Text Chest X Ray Bone Suppression For Improving Classification Of Tuberculosis Consistent Findings Html

Small Animal Thoracic Radiography Veterinary Radiology Radiography Veterinary

Cholelithiasis Cholelithiasis Radiology Gallstones
Radiographic Techniques Radiology Key

Fd Subsegmental Atelectasis Radiology Pulmonary Radiology Imaging

Fundamentals Of Radiographic Interpretation For The Dentist Pocket Dentistry
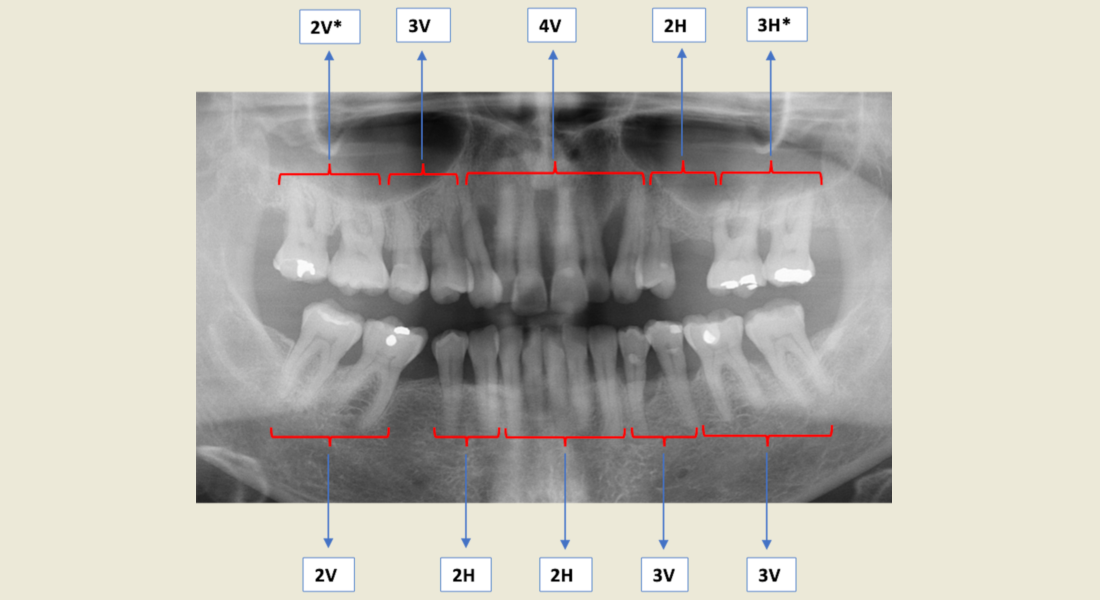
Dentistry Journal Free Full Text Development Of A Radiographic Index For Periodontitis Html
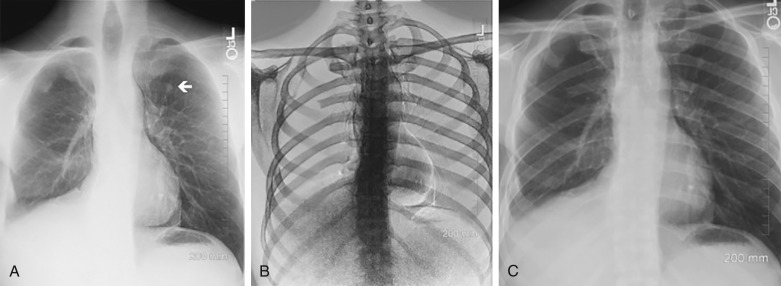
Radiographic Techniques Radiology Key

Fundamentals Of Radiographic Interpretation For The Dentist Pocket Dentistry

Hydropneumothorax Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Radiology Radiology Imaging Basic Anatomy And Physiology

Endodontic Radiography Principles And Techniques Dental Nursing
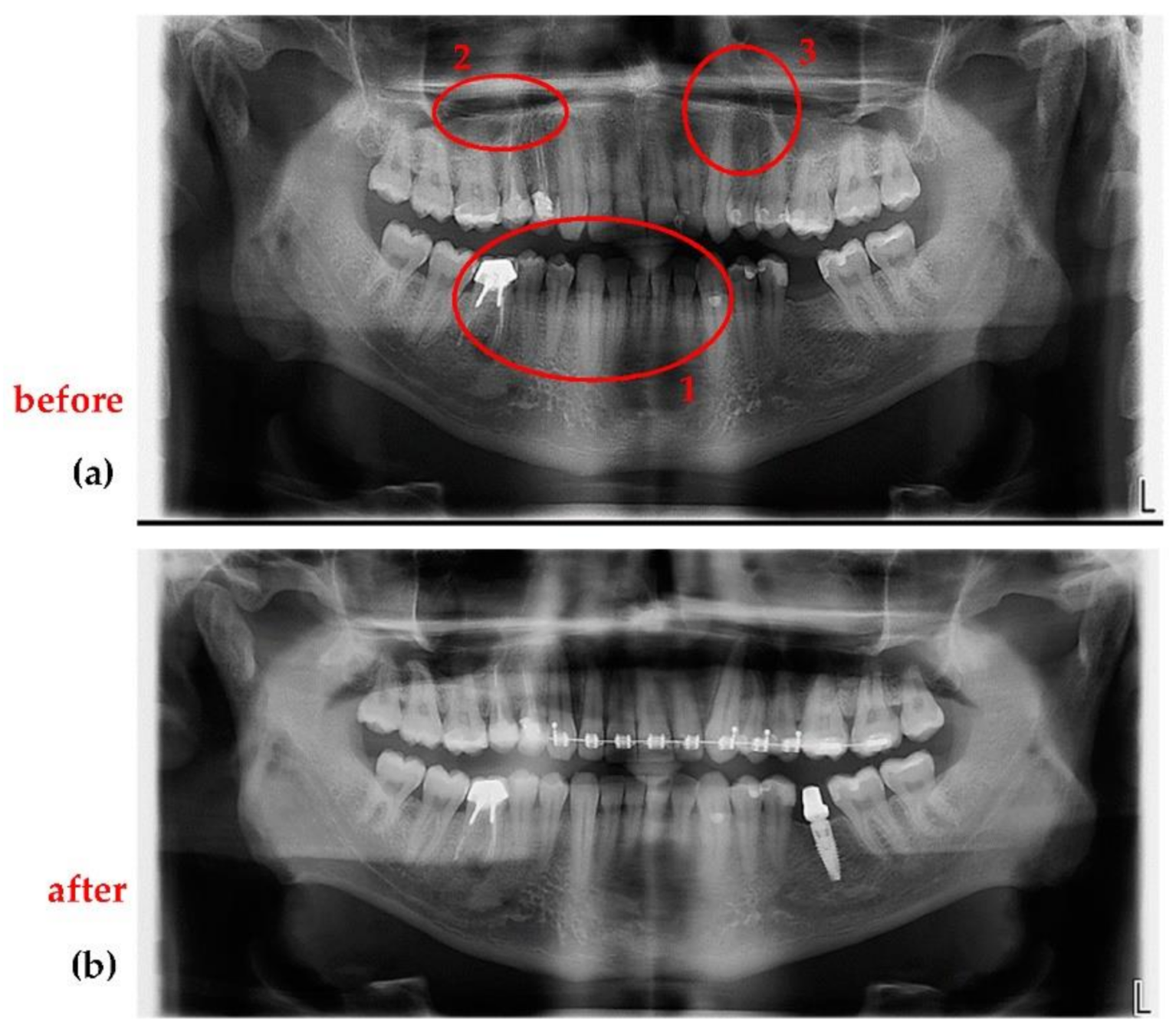
Sensors Free Full Text Optimization Of X Ray Investigations In Dentistry Using Optical Coherence Tomography Html
Radiographic Techniques Radiology Key

Atelectasis Chest X Ray Radiology Imaging Medical Radiography Radiology

Fundamentals Of Radiographic Interpretation For The Dentist Pocket Dentistry
Radiographic Techniques Radiology Key

Virtual Grid Adapts Contrast On X Rays To Improve Quality Of Exams Taken Without A Grid Itn Online Human Body Anatomy X Ray Radiology
Comments
Post a Comment